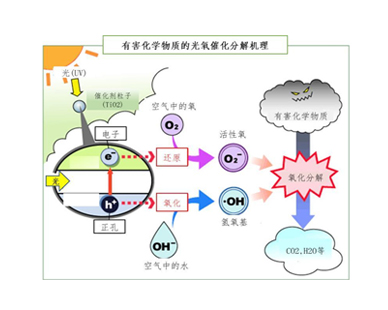

由于二氧化钛等光催化剂为半导体,因此当它接收光能时,它的价态电子会被励起成高能态并发出电子。 如果 此时接收到的能量足够高,则价态带中的电子(e-)会跃起形成传导带,参与氧和有机物的氧化反应。 由于电子跃升的能量是从光获取的,所有获取的能量与光的波长有关(即E=hv=hc/λ)。对于二氧化钛光催化剂而言,电子跃升需要比紫外线的波长(400nm)短的波长,因此,通常的光氧催化装置均使用紫 外线灯作为光源。随着技术的进步,最近能利用可见光的光氧催化剂也已经出现。
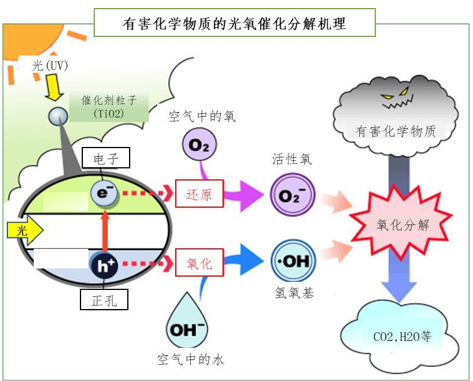
Since the photocatalyst such as titanium dioxide is a semiconductor, when it receives light energy, its valence electrons will be excited into a high-energy state and emit electrons. If the energy received at this time is high enough, the electron (e-) in the valence band will jump to form a conduction band and participate in the oxidation reaction of oxygen and organic matter. Since the energy of the electron jump is obtained from the light, all the energy obtained is related to the wavelength of the light (ie E=hv=hc/λ). For the titanium dioxide photocatalyst, the electron jump needs a wavelength shorter than the wavelength of ultraviolet (400nm). Therefore, the usual photo-oxygen catalytic devices use ultraviolet lamps as the light source. With the advancement of technology, photooxygen catalysts that can utilize visible light have also appeared recently.
全国咨询热线
地址:山东省烟台市福山区福新路96号
电话:0535-2133512
手机:18653185598
手机:13022733777
邮箱:sd_kfy@cnkaifengyuan.com

微信扫一扫

手机官网